In today’s interconnected global Halal economy, a product certified in Malaysia can be on a shelf in Dubai, Jakarta, or London within days. Yet, its Halal integrity faces its greatest test not in the factory, but in the labyrinth of the global supply chain—inside shipping containers, air cargo holds, and refrigerated trucks.
A product’s Halal integrity is tested first during transportation and then again at its next critical point: secure storage. While this guide focuses on the moving phase, the principles of custody continue in the warehouse.
The moment a Halal product leaves its certified origin, it enters a shared, often uncontrolled, logistical environment. This is where MS2400-1:2019 – Halal Transportation becomes your operational bible. It’s not just a Malaysian standard; it’s the critical protocol for any business aiming to protect its Halal certification across borders and custodians.
This guide moves beyond theory. We dissect the common critical control points in transportation and provide a actionable framework for implementation, turning a major vulnerability into your most reliable guarantee.
Why Halal Transportation is a Global Supply Chain Imperative
The Halal market is projected to be worth trillions, driven by consumer demand for guaranteed integrity. A single, verified breach in transportation can trigger:
International Recalls: Costly and brand-destroying events.
Loss of Cross-Border Market Access: Import authorities and retailers demand verifiable Halal supply chains.
Erosion of Consumer Trust: In the digital age, a logistics failure can become a global reputation crisis overnight.
MS2400-1 provides the universal “language” of controls that manufacturers, 3PLs, freight forwarders, and importers can align on, ensuring seamless Halal custody from point A to point B, anywhere in the world.
The 4 Critical Control Points in Halal Transportation & How to Secure Them
Based on MS2400-1, these are the non-negotiable areas where your operational focus must lie.
Critical Point 1: Vehicle & Equipment Suitability & History
The Risk: Invisible residues from previous non-Halal cargo (e.g., alcohol, animal fats, haram pharmaceuticals) can contaminate subsequent loads.
The MS2400-1 Requirement: Transport units must be dedicated, cleanable, and their usage history known and documented.
Implementation Checklist:
- Create a Vehicle Profile: Document the history of each unit. Prefer dedicated units for Halal goods.
- Pre-Load Inspection: Mandate a documented cleaning verification check before loading Halal cargo.
- For Shared Units: Implement a robust cleaning and validation procedure after any non-Halal use, with records.
Critical Point 2: Load Segregation & Consolidation (The “Mixed Load” Dilemma)
The Risk: Physical contact or airborne cross-contamination between Halal and non-Halal (or hazardous) goods in the same container or truck.
The MS2400-1 Requirement: Segregation must be physical, complete, and documented. This applies to full loads, groupage (LCL), and consolidated air freight.
Implementation Checklist:
- Physical Barriers: Use sealed partitions, bulkheads, or dedicated containers/pallets within a shared space.
- Stacking Protocol: Halal goods must always be placed above non-Halal goods if in the same space to prevent drip contamination.
- Documentation: The Bill of Lading or Air Waybill must clearly state the Halal status and list all co-loaded goods.
Critical Point 3: Cleaning, Sanitation & Sertu Procedures
The Risk: Standard cleaning removes dirt, but not najs (ritual impurity). Contamination from najs mughallazah (e.g., dogs, pigs) requires specific ritual cleansing (sertu).
The MS2400-1 Requirement: Organizations must have procedures for general cleaning and for sertu, performed by trained personnel.
Implementation Checklist:
- Two-Tiered SOPs: Develop separate, clear procedures for
- 1) General post-use cleaning and
- 2) Sertu for specific contamination.
- Trained Personnel: Designate and train Muslim staff or supervisors on the correct 7-step sertu method with water and soil.
- Verification Records: Maintain logs with before/after photos, cleaning agent details, and supervisor verification signatures.
Critical Point 4: The Chain of Custody & Documentation
The Risk: A broken paper trail means a broken Halal guarantee. You cannot prove integrity without proof of control.
The MS2400-1 Requirement: A documented chain of custody must be maintained from consignor to consignee.
Implementation Checklist:
- Halal Transport Document (HTD): Augment standard shipping docs with a Halal Status Certificate and Vehicle Cleaning Certificate.
- Digital Trail: Leverage IoT (Internet of Things) seals and GPS logs to provide tamper-evident, real-time custody data.
- Receiving Protocol: The consignee must verify all documents before accepting goods, rejecting any with incomplete paperwork.
Building Your Halal Transportation Compliance Plan: A 5-Step Framework
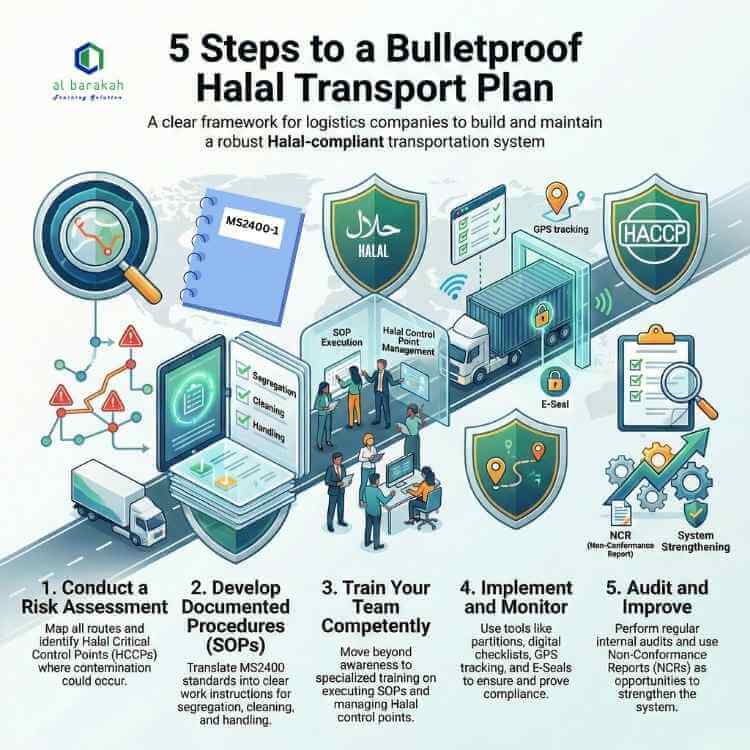
Conduct a Risk Assessment: Map all your transport routes and modes. Identify every touchpoint where contamination could occur.
Develop Documented Procedures (SOPs): Create clear, simple SOPs for each Critical Control Point above. Translate MS2400-1 clauses into work instructions for drivers and loaders.
Train Your Team Competently: Move beyond Halal awareness and foundation. Use our specialized Halal Assurance in Logistics & Supply Chain Training to equip your logistics staff with the competency to execute these procedures.
Implement & Monitor: Roll out SOPs with the necessary tools (cleaning stations, partitions, digital checklists). Supervisors must actively monitor compliance.
Audit & Improve: Schedule regular internal audits of your transport operations. Treat every non-conformance as a learning opportunity to strengthen the system.
From Cost Center to Competitive Advantage
Halal transportation compliance under MS2400-1 is not a bureaucratic burden—it is a powerful investment in supply chain resilience and brand equity. In a global market where Halal integrity is paramount, the company with the certified, auditable, and robust logistics network doesn’t just avoid risks; it wins contracts and builds unshakeable consumer trust.
Successfully navigating transportation compliance sets the stage for the next challenge. To ensure your products remain protected once they stop moving, it’s essential to master the requirements for Halal warehousing and storage.
Your logistics fleet is now a mobile ambassador of your Halal commitment. Ensure it’s equipped with the right knowledge.
Ready to transform your transport operations?
- Explore our Halal Logistics & Supply Chain Training Program for practical, MS2400-aligned competency
Need a gap analysis? Contact our Halal Logistics Consultants for a tailored review.






