The Ultimate Guide to Halal Certification in Malaysia
In today’s global marketplace, the Malaysia Halal certification is more than a religious compliance label; it is a powerful symbol of quality, safety, and integrity trusted by billions of Muslims and non-Muslims worldwide. Recognized for its rigorous standards and robust governance by JAKIM, this certification is a key that unlocks access to the rapidly growing global Halal economy, estimated to be worth trillions of dollars. For businesses in Malaysia and those exporting to Muslim-majority nations, it is not merely an advantage—it is a critical commercial imperative.
Navigating the path to obtaining your Halal certificate, however, can seem like a complex maze of regulations, paperwork, and specific procedures. The process involves multiple stages, from understanding the prerequisites to preparing for the final audit, and many businesses struggle with where to begin or how to ensure their application is successful.
This guide is designed to be your definitive, one-stop resource. We will demystify the entire Halal certification process in Malaysia, providing you with a clear, step-by-step walkthrough. From the initial eligibility requirements and cost structure to the final audit and renewal process, consider this your comprehensive manual to achieving JAKIM Halal certification with confidence.
What is Halal Certification and Why is it Important?
In its essence, a Halal certificate is an official document issued by an accredited Islamic body, like JAKIM in Malaysia, that guarantees a product, service, or system is permissible for consumption and use according to Islamic Law (Shariah). For businesses, it is far more than a logo on packaging; it is a rigorous, end-to-end assurance system that covers every stage of the supply chain—from raw material sourcing and ingredients to processing, handling, storage, and distribution.
Obtaining this certification is not a passive exercise. It requires a proactive commitment to establishing a Halal Assurance System (HAS) within your organization. This systematic approach ensures ongoing compliance and is a fundamental requirement for any company serious about achieving and maintaining its Halal status.
The strategic importance of this certification translates into direct, tangible benefits for your business:
Access to Global Markets: The Halal market is a vast, global ecosystem. A JAKIM-certified Halal certificate is one of the most recognized and respected in the world, serving as a passport to export to Muslim-majority nations and tap into the spending power of Muslim consumers everywhere. JAKIM;s Halal logo is considered “Gold Standard” for halal certification.
Enhanced Consumer Trust & Brand Reputation: The Halal logo is a universally recognized symbol of purity, hygiene, and quality control. It reassures all consumers—Muslim and non-Muslim alike—that your products are manufactured to the highest standards of safety and integrity.
Improved Operational Standards: The process of implementing a Halal Assurance System inherently leads to better hygiene, stricter quality control, and more disciplined documentation and traceability practices. This elevates your overall operational excellence.
Competitive Advantage: In a crowded marketplace, Halal certification allows your brand to stand out. It demonstrates a commitment to inclusivity and ethical compliance, giving you a significant edge over non-certified competitors.
The Governing Bodies: Understanding JAKIM and HALAL Malaysia
Navigating the Halal landscape in Malaysia begins with understanding the key authorities. The system is designed for clarity and centralized control, ensuring the integrity of the certification is never compromised.
1. JAKIM (Department of Islamic Development Malaysia) / JAIN (State Islamic Religious Department)
JAKIM/JAIN is the ultimate governing body and sole authority for the administration and development of Islamic affairs in Malaysia, and this includes Halal certification. Their specific roles are:
Setting Standards: JAKIM establishes and updates the official Halal standards (MS1500:2019) together with Department of Standards Malaysia that all applicants must adhere to. Also the latest revision of Manual Prosedur Pensijilan Halal Malaysia (DOMESTIK) 2020 (MPPHM 2020) and Malaysian Halal Management System (MHMS) 2020.
Accreditation: JAKIM accredits and oversees Foreign Halal Certification Bodies (FHCB) and Halal Certifying Bodies (HCB) for local and international applications.
Audit and Enforcement: JAKIM conducts audits, issues the final certification, and has the power to suspend or revoke certificates for non-compliance. A successful audit requires meticulous preparation. We have created a comprehensive step-by-step checklist to ensure you are fully prepared for your external JAKIM assessment.
Maintaining the Hub: JAKIM manages the MyeHalal portal, where all applications are processed.
When you search for jakim halal certification, you are looking for the official source of truth, and this guide is built upon their requirements.
2. The HALAL Malaysia Logo
The HALAL Malaysia logo is the visual representation of a JAKIM-issued certificate. It is a protected trademark, and its use is strictly regulated. Displaying this logo on your product is the ultimate proof of your compliance and grants you instant recognition and trust in the market.
Crucial Point for Businesses: It is illegal to use any Halal logo or claim on your products in Malaysia without a valid certificate from JAKIM or an accredited body. Ensuring you follow the correct process is not just about market access—it’s about legal compliance.
Halal Certification Requirements: Are You Eligible?
Before embarking on the application process, a business must first ensure it meets the foundational requirements set by JAKIM. These requirements are comprehensive, covering every aspect of the operation. Failure to meet any of these can result in a rejected application or a failed audit.
1. Product-Based Requirements
The core of your product must be Halal. This involves:
Ingredients & Raw Materials: Every single ingredient, including additives, processing aids, and flavorings, must be from a Halal source and itself be Halal. This requires diligent verification and often obtaining Halal certificates for your own raw materials from your suppliers.
Cross-Contamination: The product must be free from any contamination with non-Halal elements (e.g., pork, alcohol) throughout the entire process.
2. Process-Based Requirements
How your product is made is as important as what it’s made from.
Manufacturing & Processing: Equipment, machinery, and production lines must be purified according to Shariah law if they were previously used for non-Halal production.
Storage, Transportation & Display: Halal products must be stored, transported, and displayed in a manner that prevents any contact or cross-contamination with non-Halal items.
3. Personnel-Based Requirements
This is a critical, and often overlooked, aspect of eligibility.
The Halal Executive: JAKIM mandates that a company must appoint at least one Muslim Halal Executive. This is not a symbolic role. The Halal Executive is responsible for overseeing and ensuring the company’s daily compliance with the Halal Assurance System.
Halal Competency: The Halal Executive, and the staff involved in handling the product, must be formally trained in Halal principles and the practicalities of maintaining a Halal system. This is not optional. Proof of competency, such as a certificate from a recognized Halal Awareness Training program, is a fundamental part of a successful application.
This last point regarding trained personnel is where your journey truly begins. Establishing a competent team is the first concrete step toward certification. Sufficient training is important for every role and responsibilities, therefore proper planning of Halal Training is compulsory for successful Halal Assurance System.
Meeting all these requirements is the definitive benchmark for a successful Halal certificate application. Given the detailed nature of these standards, how can a business be certain it’s ready?
A strategic first step is to undergo a Halal Gap Analysis. This service is designed to answer that critical question. We systematically evaluate your eligibility across all JAKIM’s criteria—Location, Premise layout, product & raw materials, process, Documents and personnel—providing you with a detailed report and a prioritized checklist to achieve full compliance.
The Step-by-Step Halal Certification Process
Understanding the official procedure is key to a smooth and successful application. The entire Halal certification process in Malaysia is designed to be systematic and thorough, ensuring only fully compliant businesses receive the esteemed HALAL Malaysia logo. The following flowchart provides a clear, high-level overview of the journey, which we will then break down in detail.
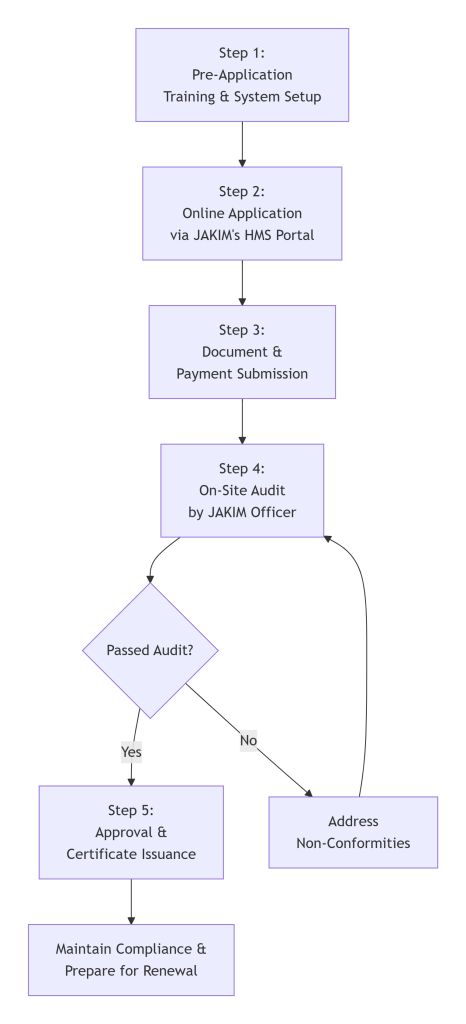
Step 1: Pre-Application (The Foundation: Training and System Setup)
This is the most critical phase, where the groundwork for your application’s success is laid. Rushing this step is the most common reason for application rejection or audit failure.
Halal Team Appointment & Training: As mandated in the requirements, you must appoint your Muslim Halal Executive (for a company that requires Halal Assurance System) and ensure they, along with relevant staff, have undergone certified Halal Awareness Training. This training provides the essential knowledge to implement and manage the Halal system correctly.
Establish an Internal Halal Control System (IHCS): This is your company’s internal framework to ensure ongoing Halal compliance. It involves developing documented procedures, control points, and records for all aspects of your operations, from sourcing to shipping.
Conduct a Halal Gap Analysis (Highly Recommended): Before you ever log into the application portal, a professional Halal Gap Analysis is the single best way to de-risk your investment. This service acts as a mock audit, identifying weaknesses in your system, documentation, and readiness, giving you a clear and actionable roadmap to fix them before the official JAKIM audit.
✅ Actionable Tip: Do not proceed to Step 2 until your internal system is robust and your team is fully trained. This preparation directly influences the speed and success of all subsequent steps.
Step 2: Online Application via the MyeHalal
All applications are submitted digitally through JAKIM’s MyeHalal portal. You will need to create an account and fill in the detailed application form, which requires information about your company, the products to be certified, and your manufacturing processes.
Step 3: Document and Payment Submission
After the initial online form, you will be required to submit a comprehensive set of supporting documents. This typically includes:
Company registration documents
Manufacturing license
Detailed product information and ingredient lists
Floor plans of your facility
Flowcharts of your manufacturing process
Proof of your Halal Executive’s training certificate
Your documented Internal Halal Control System (IHCS) manual
Once the documents are verified, you will be required to pay the official Halal certificate cost as stipulated by JAKIM.
Step 4: The On-Site Audit by JAKIM
This is the verification stage. A JAKIM officer will schedule and conduct a thorough audit of your premises. They will:
Inspect all facilities, equipment, and storage areas.
Review all your records and documentation for accuracy and compliance.
Interview your Halal Executive, Halal Supervisors or Halal personnel and staff to verify their understanding and competency.
Step 5: Approval and Certificate Issuance
If your application and audit are successful, JAKIM will issue your Halal certificate, which is typically valid for two years. You will be authorized to use the HALAL Malaysia logo on your certified products according to the strict guidelines provided.
The process does not end here. Maintaining your certification requires ongoing adherence to the system you have built, including preparing for renewal audits before your certificate expires.
Understanding the Costs: Halal Certificate Fees and Budgeting
A common question we encounter is, “How much does a Halal certificate cost in Malaysia?” It’s essential to distinguish between the official JAKIM fees and the total investment required for your business to achieve compliance. Proper budgeting from the outset prevents unexpected financial strain.
Official JAKIM Halal Certificate cost Fees: Among the Lowest in the World
It is important to recognize that the direct fee paid to JAKIM is highly subsidized and is, in fact, among the lowest in the world, starting from just RM 100 per year for a micro-enterprise and RM200 for halal certification for small business. This makes Halal certification highly accessible. The fee structure is based on your company’s paid-up capital, as outlined below.
| Halal Scheme | KATEGORI | FI (RM)/ | |
| Produk dan Perkhidmatan Makanan dan Minuman, Kosmetik, Farmaseutikal, Barang Gunaan, Logistik, Pengilangan Kontrak/ OEM, Peranti Perubatan, Dapur Berpusat. | INDUSTRI | CIRI-CIRI | TAHUN |
| Mikro | Nilai perolehan tahunan kurang daripada RM300,000.00 | 100 | |
| Kecil | Nilai perolehan tahunan daripada RM300,000.00 hingga RM14,999,999.99 | 400 | |
| Sederhana | Nilai perolehan tahunan daripada RM15 Juta hingga RM50 Juta | 700 | |
| Besar | Nilai perolehan tahunan melebihi RM50 Juta | 1,000 | |
The Total Investment: The Real Cost of Readiness and Compliance
While the JAKIM fee is minimal, applicants must understand that certification involves other essential costs to become fully compliant. The JAKIM fee is for the certification itself; the following investments are to ensure your business is ready for it.
Premise Renovation & Compliance: Many businesses, especially in the food industry, need to invest in facility upgrades to adhere to foundational guidelines like Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and food safety standards. This can include costs for structural changes, equipment segregation, and installing dedicated hygiene stations, which are all prerequisites for a Halal environment.
Training & Capacity Building: This is a multi-layered investment in your human capital. It includes:
Foundational courses like Food Handling Training and mandatory Halal Awareness Training.
Advanced competency programs such as Halal Competency Training and the Halal Executive Program.
Specialized training like the High-Impact Halal Executive Training, designed for professionals who need the advanced, practical skills to develop and manage a Halal Assurance System from scratch.
- Consultancy & Advisory Services: Choosing a Safe and Recognized Partner
Many businesses benefit from the initial guidance of professional Halal consultant services to develop the required documentation and system frameworks correctly the first time, avoiding costly mistakes.
⚠️ A Critical Warning for Applicants:
Be highly aware of opportunists and scammers who act as consultants. A common tactic is to request large upfront deposits but fail to deliver any substantive work, leaving businesses with financial loss and significant delays in their certification journey.✅ The Safe Path: JAKIM & MIHA Recognized Consultants
To protect applicants, JAKIM, through the Malaysia International Halal Academy (MIHA), maintains a registry of registered and recognized Halal consultants. These consultants have undergone vigorous registration procedures, including comprehensive Train-the-Trainer (ToT) programs, ensuring they are qualified and adhere to strict ethical and professional standards.Al-Barakah is a proud recognized strategic partner of MIHA. Our consultant team is comprised of certified professionals who have successfully passed these rigorous requirements. When you engage our >professional Halal consultancy services, you are not just hiring an advisor; you are partnering with a trusted entity that is formally acknowledged by the governing bodies of Halal in Malaysia. Your investment is safe, and your path to certification is secure.
Gap Analysis Service: An upfront investment in a Halal Gap Analysis (RM250-500) is a strategic move that can save significant money and time by providing a clear snapshot of your readiness and a prioritized action plan before you engage in major renovations or face a formal audit.
Strategic Insight: View these costs not as an expense, but as an investment into your company’s quality infrastructure, operational excellence, and market access capabilities. The return, in the form of new customers, enhanced brand trust, and improved processes, far outweighs the initial outlay.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
The path to Halal certification is rigorous, and it’s common for businesses to encounter obstacles. Recognizing these challenges early is the first step toward overcoming them. Here are the most frequent hurdles and our expert advice on how to navigate them successfully.
Challenge 1: Overwhelming and Complex Documentation
The Problem: Many applicants struggle with the sheer volume and specificity of documentation required for the Internal Halal Control System (IHCS). Understanding what policies, procedures, and records are needed—and how to write them correctly—can be a major bottleneck.
The Solution: Do not start from a blank page. Use established frameworks and templates. Investing in our Halal Gap Analysis service provides you with a detailed checklist of required documents. Furthermore, our Halal Consultant services can develop this entire documentation suite for you, ensuring it is audit-ready.
Challenge 2: Lack of Competent Halal Personnel
The Problem: JAKIM’s requirement for a trained Muslim Halal Executive / Halal Supervisor is clear, but finding or developing a staff member with the right competency is difficult. Simply appointing someone without proper training often leads to a failed audit.
The Solution: This is a core problem we solve. Enroll your key staff in our foundational Halal Awareness Training to meet the basic requirement. For the individual responsible for developing and managing the entire system, our High-Impact Halal Executive Program or Halal Competency Training provides the deep, practical knowledge needed for success.
Challenge 3: Facility and Infrastructure Non-Compliance
The Problem: Existing facilities, especially those that have handled non-Halal products, often require significant physical changes to prevent cross-contamination. This includes segregated production lines, dedicated storage, and purified equipment.
The Solution: Early engagement is key. A Halal Gap Analysis includes a facility review that will identify all physical gaps before you invest in renovations. Our consultants can then advise on the most cost-effective ways to achieve compliance, saving you from costly corrective actions later.
Challenge 4: Managing the Supply Chain and Raw Materials
The Problem: Ensuring every single ingredient and raw material is Halal-certified from its source is a massive task. Verifying the authenticity of suppliers’ Halal certificates and maintaining a chain of custody is complex.
The Solution: Implement a robust supplier approval procedure as part of your IHCS. We cover the practical steps of supplier verification in our Halal Assurance System (HAS) training. This empowers your Halal Executive to manage this critical process effectively.
Challenge 5: Failure During the JAKIM Audit
The Problem: The stress of the official audit can lead to mistakes. Auditors are trained to spot inconsistencies between your documentation and actual practices, as well as a lack of understanding among staff.
The Solution: Preparation is everything. Beyond training, consider our Halal Internal Audit Training to teach your team how to conduct your own internal audits. This acts as a “dress rehearsal” for the real JAKIM audit, identifying and fixing issues proactively. For the ultimate preparation, our Halal Assurance System (HAS) Review Training is designed specifically to prepare you for the final assessment.
Key Takeaway
The most successful applicants view these challenges not as barriers, but as phases of a structured project. By understand this process and requirements, you gain a roadmap that anticipates these hurdles and provides proven solutions, turning potential failures into guaranteed successes.






