For logistics managers, warehouse supervisors, and supply chain directors in Malaysia, a new critical question has emerged: Is your supply chain Halal-compliant?
A product can be manufactured to perfect Halal standards, yet its integrity can be irrevocably compromised during transportation, storage, or handling. Shared containers, improper vehicle cleaning, mixed-load segregation failures, and inadequate warehouse zoning are not just operational headaches—they are direct threats to your Halal certification under the latest Malaysian standards.
The Halal Supply Chain Management System (HSCMS) MS2400:2019 is the definitive framework that addresses this gap. This guide serves as your comprehensive manual to MS2400-1:2019 (Transportation), MS2400-2:2019 (Warehousing) and MS2400:3:2019 (Retailing) providing the clarity and actionable steps needed to transform your logistics network from a vulnerability into a verified pillar of Halal assurance.
Why Halal Logistics is Non-Negotiable
The Integrity Gap: “From Farm to Fork”
The Halal journey does not end at the factory gate. The supply chain—transport, storage, cross-docking—is fraught with contamination risks (najs) that can nullify a product’s Halal status. MS2400:2019 exists to close this integrity gap, ensuring custodianship (amanah) is maintained at every handover point.
The Business Imperative
Regulatory Compliance: JAKIM and Halal certification bodies now scrutinize supply chain controls. Non-compliance with MS2400 can lead to audit findings and certification risks.
Brand & Financial Protection: A single cross-contamination incident in logistics can trigger massive product recalls, destroy consumer trust, and devastate your brand in key Muslim markets.
Competitive Advantage: Demonstrating certified Halal logistics capability is a powerful differentiator for logistics service providers (LSPs) and a critical due-diligence factor for Halal brand owners.
Demystifying the MS2400:2019 Standards
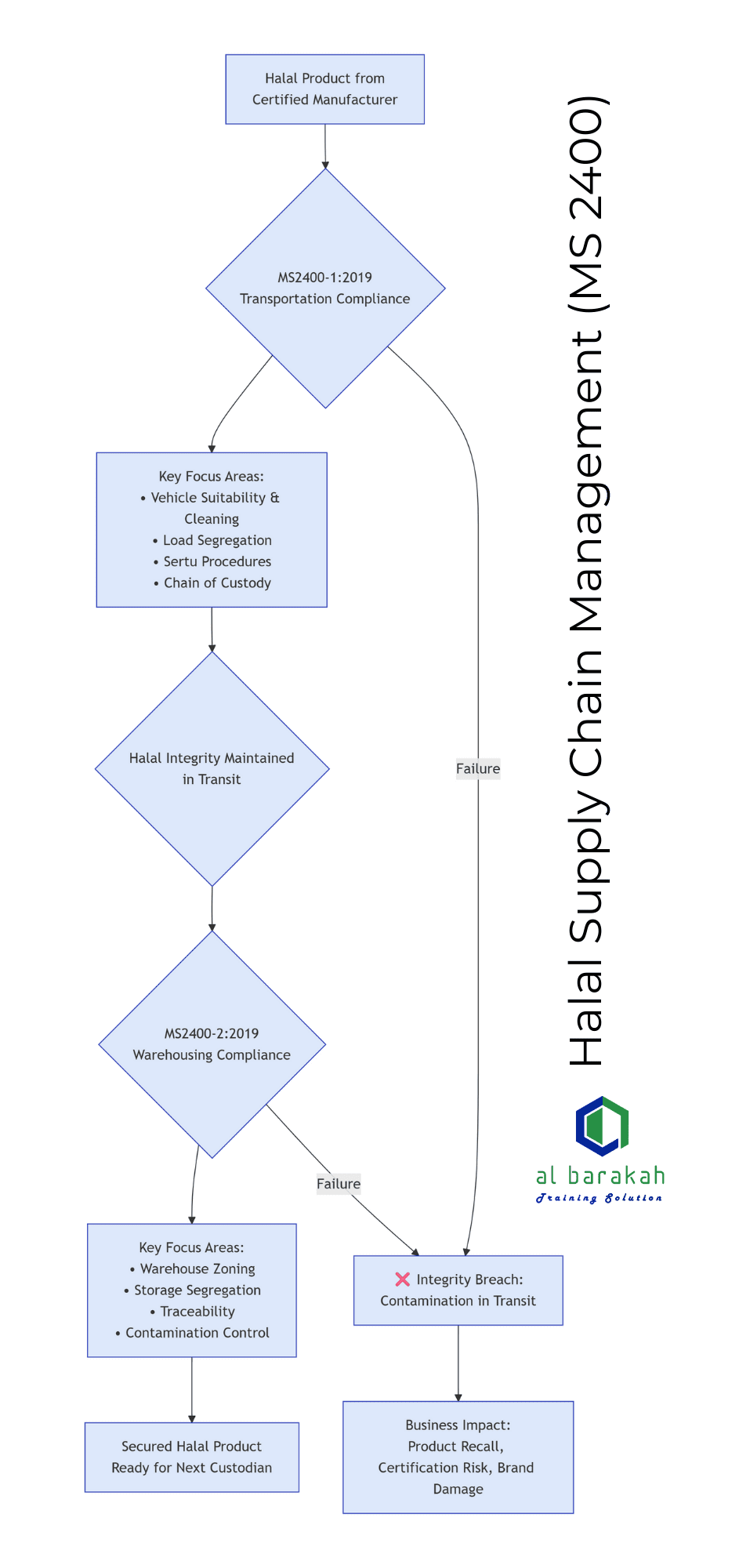
MS2400 is a trilogy, but the operational core for logistics lies in Parts 1 and 2.
MS2400-1:2019: Halal Transportation – General Requirements
This standard governs the movement of Halal goods. Its core principle is preventing contamination during transit.
Key Operational Requirements Include:
Vehicle & Equipment Suitability: Ensuring transport units are dedicated, cleanable, and free from prior non-Halal cargo contaminants.
Segregation During Consolidation: Implementing strict procedures for mixed loads (Halal with non-Halal or Halal with hazardous materials) to prevent physical and cross-contamination.
Control of Outsourced Carriers: Your responsibility extends to your subcontractors’ and agents’ compliance.
Critical Documentation: Maintaining a verifiable chain of custody through transport documents, proof of delivery, and cleaning records.
Procedure for Sertu: Mandating the correct ritual cleansing process for vehicles/equipment contaminated with najs mughallazah (e.g., from dogs or pigs).
MS2400-2:2019: Halal Warehousing – General Requirements
This standard governs the storage and handling of Halal goods within a facility. Its core principle is maintaining integrity during static phases.
Key Operational Requirements Include:
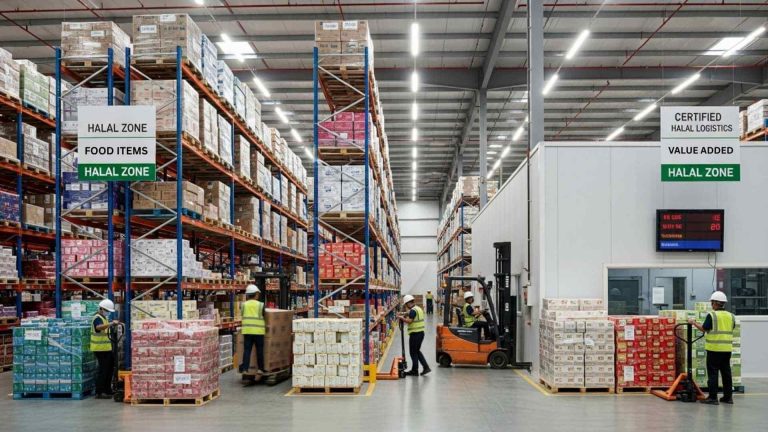
Physical Warehouse Zoning: Defining and segregating areas for Halal, non-Halal, and quarantine storage. This includes clear signage and access controls.
Stock Management & Traceability: Systems to ensure FEFO/FIFO while maintaining Halal status, and full traceability from receipt to dispatch.
Pest Control & Hygiene: Aggressive programs to prevent infestation and maintain a clean environment that protects goods.
Handling of Non-Conforming Stock: Established procedures for isolating and disposing of contaminated, affected, or doubtful products.
Personnel Hygiene & Training: Specific protocols for staff handling Halal goods, including cleanliness and dedicated training.
Halal Supply Chain Management in Retailing: Ensuring Integrity at the Final Frontier
The retail environment represents the crucial final touchpoint in the Halal supply chain—the stage where products directly meet the consumer. MS 2400-3:2019 – Halal Supply Chain Management System – Part 3: Retailing establishes the essential framework for preserving Halal integrity at this most visible and vulnerable junction.
This standard translates the principles of Shariah-compliance into actionable management system requirements specifically tailored for retail operations, ensuring that the Halal status of goods is maintained from the moment they are received at the store until they are purchased by the end-user.
Building upon the foundations laid in transportation (Part 1) and warehousing (Part 2), this pillar addresses the unique complexities of the retail space, where Halal and non-Halal products may coexist, and where customer interaction, display, and final handling present distinct risks of contamination or compromise.
It provides retailers with a systematic approach to manage these risks through clear responsibilities, documented procedures, controlled processes, and continuous verification, ultimately safeguarding consumer trust and fulfilling both religious obligations and regulatory expectations in the marketplace.
The Common Pitfalls & How to Avoid Them
Many first-time implementers stumble on the same issues:
Pitfall 1: Assuming “general cleanliness” equals Halal compliance.
- Solution: Implement Halal-specific risk assessment to identify unique najs contamination points (e.g., previous cargo, pallet sharing, condensate drip).
Pitfall 2: Inadequate training for ground staff (loaders, forklift drivers, warehouse clerks).
- Solution: Move beyond awareness to competency-based training on specific procedures like segregation checks and incident reporting.
Pitfall 3: Poor documentation that breaks the chain of custody.
- Solution: Integrate Halal status checks and cleaning records into existing Good Distribution Practice (GDP) or warehouse management system workflows.
Your Strategic Pathway to Compliance
Achieving compliance is a systematic process, not a one-time event.
Phase 1: Gap Analysis & Scope Definition
Conduct a review of current transport and warehouse operations against MS2400-1 & MS2400-2 clauses. Define the physical and process scope of your Halal Management System.
Phase 2: Develop the Halal Risk Management Plan (HRMP)
This is the core document. It must identify Halal Control Points (HCPs), evaluate contamination risks, and prescribe specific control measures, monitoring, and corrective actions for your unique operations.
Phase 3: Implementation & Staff Competency
This is where theory meets practice. It involves:
Physical Changes: Zoning, signage, dedicated equipment.
Documentation: New checklists, logs, and procedures.
Critical Component – Training: Generic Halal Awareness is insufficient. Your logistics team needs role-specific, scenario-based training on the exact procedures they must follow.
Phase 4: Internal Audit & Management Review
Before any external audit, conduct your own internal audit. Review the entire system’s effectiveness with top management to ensure ongoing commitment and resource allocation.
Specialized Training: The Engine of Successful Implementation
Your workforce is your strongest control point or your greatest vulnerability. To build true competency, a one-size-fits-all approach does not work. We recommend a structured training pathway that takes your team from foundational awareness to specialized, role-specific mastery.
Step 1: Foundational Knowledge for All
Before diving into complex procedures, every employee in the supply chain must understand the “why” behind the rules.
Halal Awareness Training for Supply Chain Personnel
This essential course provides the mandatory foundational knowledge required by JAKIM, but with a crucial difference: it is contextualized specifically for logistics, transport, and warehouse environments.
Course Focus: Moves beyond generic food principles to explain how Halal & Haram concepts apply in a supply chain context—contamination risks in shared spaces, the importance of custody (amanah), and the concept of najs (impurity) as it relates to vehicles, equipment, and storage areas.
Who It’s For: All staff—from truck drivers and loaders to warehouse clerks and security personnel. This is the non-negotiable base layer of knowledge that empowers every individual to identify red flags.
Completing this course fulfills the basic JAKIM training requirement and ensures your entire team shares a common language of Halal integrity.
Step 2: Role-Specific Competency for Key Personnel
With the foundation set, personnel with specific responsibilities need advanced, actionable skills.
Halal Assurance in Logistics & Supply Chain Training
This is the specialized, advanced program for staff who design, execute, and audit your Halal controls. The curriculum is built directly on the clauses of MS2400-1:2019 and MS2400-2:2019.
Course Focus: Translates the standards into daily operational reality. It provides the tools and procedures to actively manage Halal risks.
Who It’s For: Transport Coordinators, Warehouse Supervisors, Logistics Managers, Halal Committee Members, and Internal Auditors within the supply chain.
Practical Outcomes: Participants will learn to:
Conduct a Halal risk assessment for transport routes and warehouse layouts.
Identify, document, and monitor Halal Control Points (HCPs) in logistics workflows.
Execute and verify the correct Sertu (ritual cleansing) procedures for equipment and vehicles.
Apply rigorous receiving and dispatch verification protocols to maintain the chain of custody.
Properly segregate and document mixed loads and storage for Halal and non-Halal goods.
Develop and implement corrective actions for spillages or contamination incidents.
This two-tiered training pathway ensures compliance is not just a manual on a shelf, but a living, breathing practice embedded in your operations. It transforms your supply chain from a point of vulnerability into your most reliable asset for Halal assurance.
This structured training is essential for: Logistics Service Providers (3PL/4PL), in-house logistics departments of Halal manufacturers, cold chain operators, freight forwarders, and retailers distributing Halal products.
Ready to secure your supply chain and transform it into a competitive asset?
Speak directly with our Halal Logistics Specialist for a consultation.
Build an unbreakable global chain of trust.






