For any Malaysian small or medium enterprise (SME) considering the path to ISO 9001 certification, the journey begins with a single, crucial step: the Gap Analysis. This diagnostic process is the equivalent of a detailed business health check, revealing the distance between your current operations and the requirements of the ISO 9001:2015 standard. Conducting a thorough analysis is not merely a recommendation—it is the strategic foundation that determines the efficiency, cost, and success of your entire certification project.
This guide provides Malaysian business owners and quality managers with a clear, actionable, step-by-step framework for performing an effective ISO 9001 gap analysis, tailored to the local business context.
Why a Gap Analysis is Non-Negotiable for Malaysian SMEs
Skipping a gap analysis is like beginning construction without a blueprint. For resource-conscious SMEs, this often leads to:
Unforeseen Costs: Hidden complexities emerge mid-project, blowing budgets.
Extended Timelines: A lack of clear direction causes significant delays.
Project Fatigue: Teams become overwhelmed by unplanned work, risking abandonment of the QMS.
A proper analysis provides your ISO 9001 roadmap for Malaysia, offering a prioritized action plan, accurate budget estimation, and clear justification for management and staff.
Pre-Analysis Phase: Laying the Groundwork
Step 1: Assemble Your Core Team
Form a small, cross-functional team with a designated leader (the future Management Representative). Include members from operations, administration, and quality functions to gain a holistic view of your organisation.
Step 2: Gather Essential Documents
Collect existing documents that reflect your current “way of working”:
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
Quality policies or objectives (if any)
Training records
Previous audit reports (internal or customer)
Organizational charts
Customer complaint logs
Step 3: Secure the ISO 9001:2015 Standard
Obtain the official copy of the MS ISO 9001:2015 standard from Jabatan Standard Malaysia (JSM). This is your definitive checklist. Familiarize your team with its structure, particularly the ten core clauses (4-10).
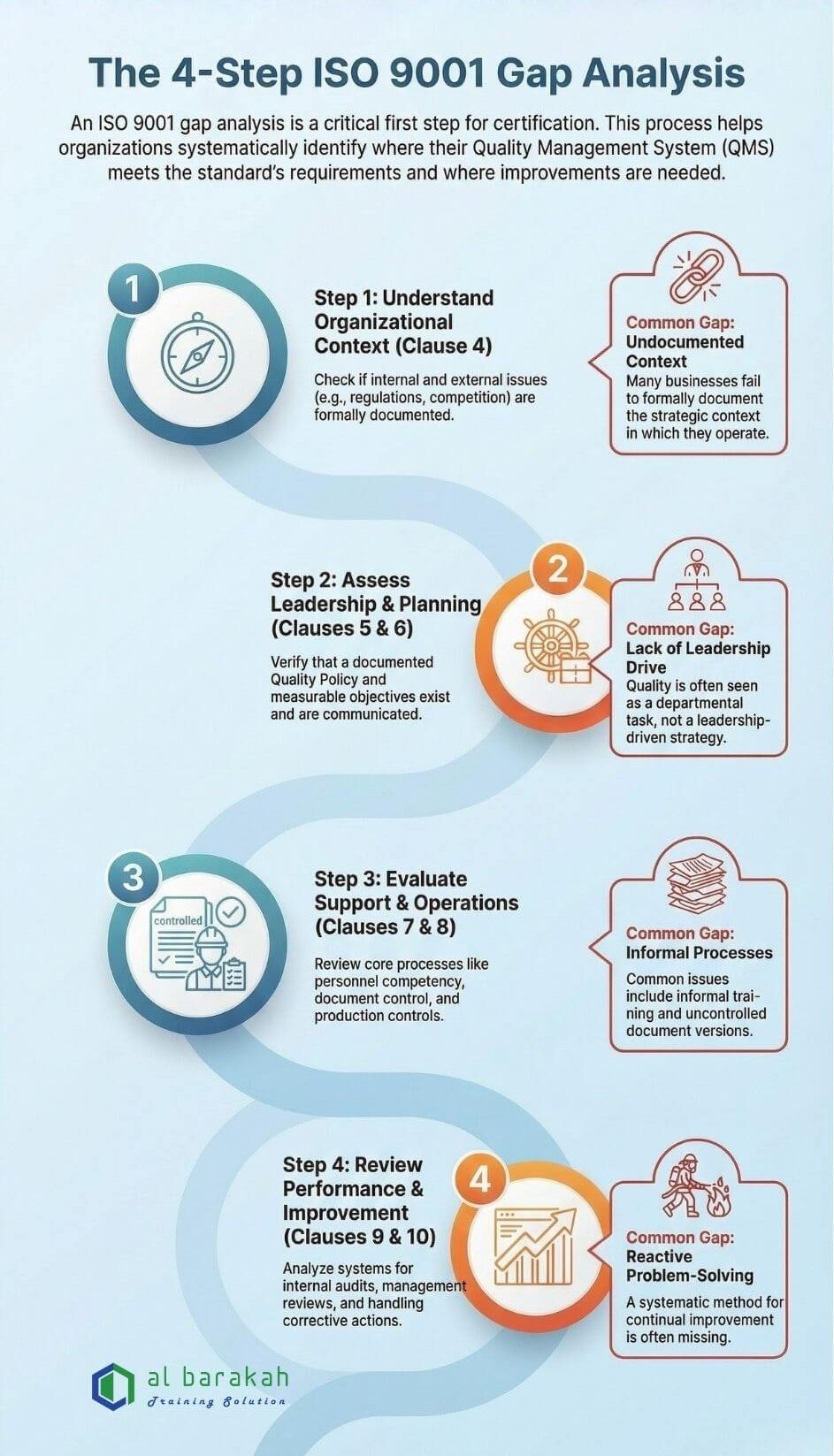
The 4-Step ISO 9001 Gap Analysis Process
Step 1: Understand Organizational Context (Clause 4)
This modern requirement asks you to document internal and external issues relevant to your strategic goals.
Check: Have we identified factors like new Malaysian regulations, market competition, or internal technological changes?
Typical Gap: Many SMEs operate without formally documenting this context, which is now a mandatory part of the QMS.
Step 2: Assess Leadership & Planning (Clauses 5 & 6)
Evaluate top management’s involvement and strategic planning.
Check: Is there a documented Quality Policy? Have measurable quality objectives been set and communicated? Has leadership demonstrated commitment?
Typical Gap: Quality is often seen as a departmental issue, not a leadership-driven strategy. Objectives may be absent or not measurable.
Step 3: Evaluate Support & Operations (Clauses 7 & 8)
This is the most extensive part, reviewing your core processes.
Check (Support): Are personnel competent and trained? Are work environments suitable? Is documented information controlled?
Check (Operations): Are customer requirements reviewed? Is design/development controlled? Are purchasing and production processes defined and controlled?
Typical Gaps: Informal training, uncontrolled document versions, and poorly defined operational processes are common findings in SMEs.
Step 4: Review Performance & Improvement (Clauses 9 & 10)
Analyse your systems for monitoring and improvement.
Check: Do we conduct internal audits and management reviews? How do we monitor customer satisfaction? Is there a process for corrective action?
Typical Gap: A reactive approach to problems is common, with no systematic method for internal auditing, management review, or driving continual improvement.
Documenting Your Findings: The Gap Analysis Report
Create a simple report table to present to management:
| ISO 9001 Clause | Requirement | Current State | Gap Identified | Priority (H/M/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.1.1 Leadership | Top management must demonstrate commitment. | Quality decisions are delegated without senior oversight. | No evidence of management driving the QMS. | High |
| 7.2 Competence | Personnel must be competent based on education/training. | Training is conducted but records are not maintained. | No formal training records or competency matrix. | Medium |
| 8.5.1 Control of Production | Production must be carried out under controlled conditions. | Relies on experienced workers without written SOPs. | Key processes are not documented or standardized. | High |
From Analysis to Action: Your Implementation Plan
The final output of your gap analysis is a prioritized Implementation Plan. This plan should sequence actions logically:
Address foundational gaps first: Start with Context and Leadership (Clauses 4 & 5) to ensure management commitment.
Develop core documentation: Create necessary policies, objectives, and SOPs for key processes.
Establish monitoring systems: Plan for internal audits and management reviews.
Consider training: A foundational ISO 9001 Awareness Training course is highly effective at this stage to align your team with the standard’s requirements and address competency gaps identified.
Once your gap analysis is complete, you will have a clear picture of which processes need the most attention. For manufacturing companies, this often highlights critical needs in production control and supplier management. A detailed, sector-specific roadmap for implementing ISO 9001 in a Malaysian factory can be found in our dedicated guide for the manufacturing sector.
Conclusion: Your Blueprint for Success
A meticulously executed ISO 9001 gap analysis is the most strategic investment you can make at the start of your quality journey. It transforms an ambiguous project into a managed, predictable process with clear deliverables. For Malaysian SMEs, it is the tool that turns the ambition of international quality certification into a achievable, step-by-step reality, building a QMS that is truly integrated and adds lasting value to your business.
Ready to take the next informed step? A gap analysis will clearly define your team’s knowledge requirements. Explore how structured learning can accelerate your implementation in our comprehensive guide, ISO 9001 in Malaysia: The Complete Guide to the Quality Management Standard.



